PIAP Space Sp. z o. o. (PIAP Space) is a Polish company established in 2017 as a spin-off of the Łukasiewicz Research Network – Industrial Institute for Automation and Measurements (PIAP Institute). Currently, the owners of PIAP Space are: Industrial Development Agency and PIAP Institute.
In its activities, PIAP Space has a strong focus on leveraging the existing heritage of mobile robotics and the ongoing research and development activities of the PIAP Institute. PIAP Space develops technologies and products in the areas of satellite integration and test equipment (MGSE), active space debris removal, manipulators and grippers, on-orbit satellite handling, human-robot interaction and sensors such as close range vision systems and F-T sensor.
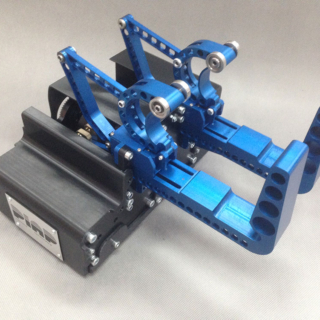
- The LAR gripper was developed as part of the EROSS and EROSS plus project. The gripper has reached technology readiness level 6 (TRL 6). Technology readiness at level 7 (TRL 7) will be achieved by the gripper during the €ROSS IOD project.
- The TITAN robotic arm (TITAN arm) has been developed as part of an ESA-supervised project. The TITAN prototype is a multi-articulated robotic arm designed for the future deorbitation and servicing of satellites in orbit.
- The Multipurpose Servicer Gripper is to be equipped with a set of robotic tools that can provide on-orbit satellite repairs by fulfilling the main functions: enhancement of visual inspection; support for antenna and solar panel deployment; insulation regeneration; module replacement. The proposed design of the multifunctional servicer gripper follows the European paradigm, which focuses on the development of versatile building blocks to create new modular robotic solutions for orbital missions and planetary exploration.
- MGSE: GHA adapters, Clampbands, Integration stands, Mass dummies, different kind of jigs.
Projects:
- Biomass Adaptor – PIAP Space is designing and manufacturing a set of three adaptors for testing and integration of the ESA Biomass satellite. Two adaptors are for thermal testing and integration of the satellite and the third for vibration testing.
- Biomass MPT – Spacecraft Container and Multi-Purpose Trolley (MPT) . – PIAP Space, together with the Italian company Elital, is designing and manufacturing two MGSEs for the ESA Biomass satellite. The first is a container for transporting the satellite from the integration hall to the launch site, the second is the MPT device for integrating the satellite.
- BIOMASS ADAPTORS – The aim of the project is to design and manufacture a set of three adapters for testing and integration of the ESA Biomass satellite. Two adapters will be for thermal testing and satellite integration and the third for vibration testing.
- EROSS + – EROSS+ is a continuation of the EROSS (European Robotic Orbital Support Services) project. The main objective of EROSS+ is to integrate the building blocks designed by previous GI projects to demonstrate the capability to operate satellites in orbit. The EROSS+ project will also increase the maturity of these key building blocks and enhance their functionality and performance in a coherent work programme aimed at rapid and practical implementation of the developed solutions in space. The project will also provide input for the evaluation of service tasks for non-cooperative orbital targets.
- ORBITA – The aim of the project is to develop a family of modular grapples for orbital and planetary applications. The project will develop three types of innovative grapples: for satellite capture, for satellite servicing and for planetary missions. The result of the project will constitute a product innovation on an international scale.
- TITAN – The project involves the development of a robotic arm for servicing satellites. The contract will include the development of a prototype of a multi-articulated robotic arm for the future deorbitation and servicing of satellites in orbit. A laboratory model of the robotic joint will be created, followed by a prototype consisting of different types of joints, which will undergo full environmental testing on a shaker, thermal and thermal-vacuum tests. Ultimately, as part of the project, a TRL6 technology readiness level will be achieved. The robotic arm developed in the TITAN project will allow the servicing of damaged satellites and the deorbitation of satellites that have reached the end of their mission time and threaten other objects in orbit. This will enable the removal of 'space debris’ that threatens the proper functioning of satellites.
- ATHENA MGSE – The objective of the ATHENA (Advanced Telescope for High-Energy Astrophysics) mission is to develop an X-ray telescope capable of answering questions on the issue of 'The Hot and Energetic Universe’ and on the Cosmic Vision campaign. In this project, PIAP Space is supplying MGSE to TAS-PL (Thales Alenia Space Poland) for the assembly, integration and testing of the prototype testbed. The aim of the project is to develop a prototype satellite design to verify some of the technical assumptions.
- €ROSS IOD – the main objective of the project is to enable the deployment of advanced space robotics to support sustainable development in space. With the technology in place to service satellites in orbit, it will be possible to extend their life cycle and improve their service life to reduce space debris. It will also be possible to manage satellites while they are operating in space. As part of the ongoing project, PIAP Space will develop a LAR (Launch Adapter Ring Gripper) for servicing satellites. €ROSS IOD is a continuation of the concluding EROSS + project. €ROSS IOD is implemented with funding from the European Union under the Horizon Europe programme.
Areas of activity in the space sector:
- Space robotics
- MGSE
Clients and partners:
- ESA
- Komisja Europejska
- POLSA
- DLR
- OHB
- Thales Alenia Space
- Airbus Defence & Space
- SAAB
- GMV
- National Technical University of Athens
- Space Applications Services
- CBK PAN
- KP Labs
- Sintef
- Spacive
- Śląskie Centrum Naukowo-Technologiczne Przemysłu Lotniczego